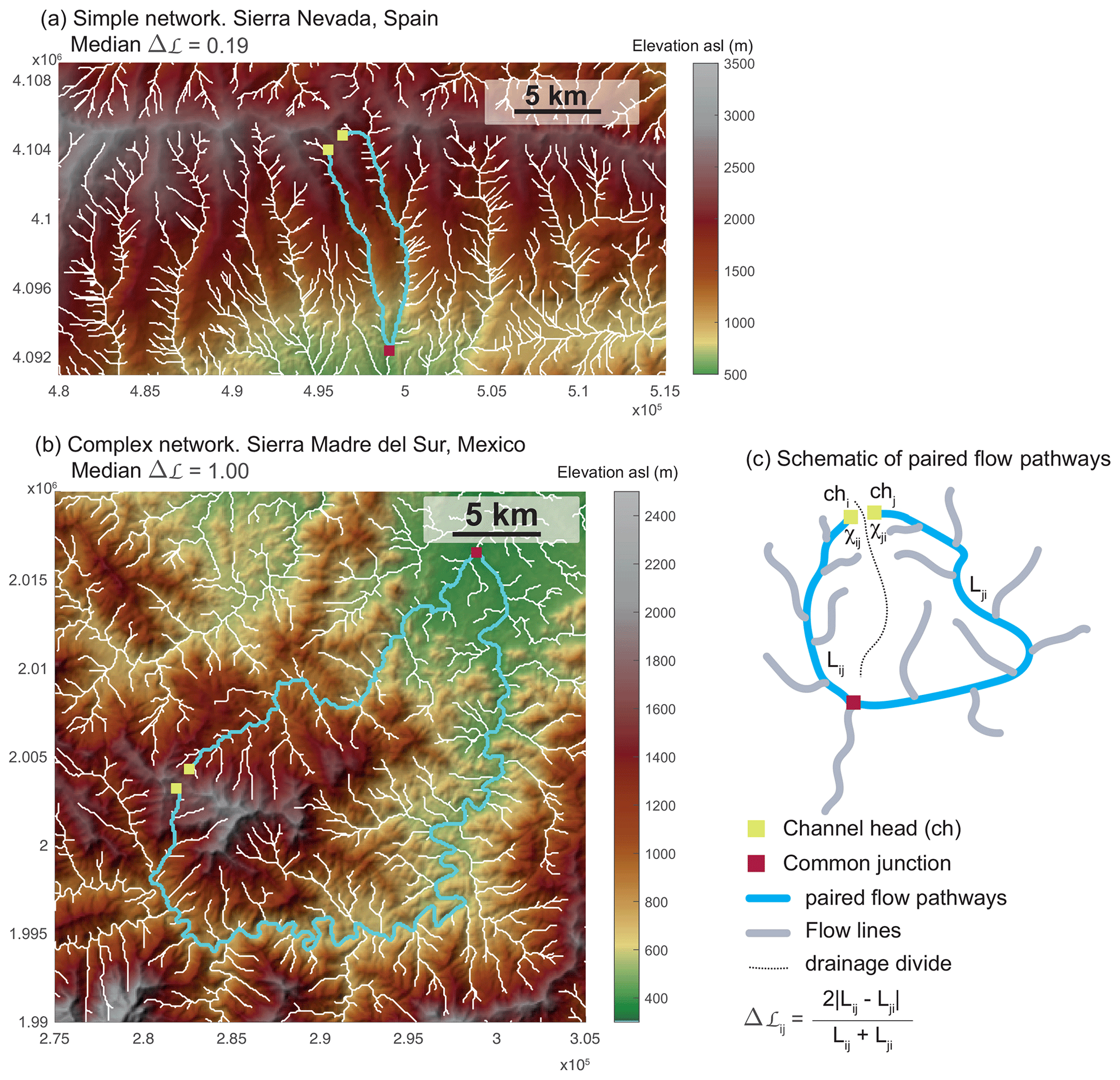
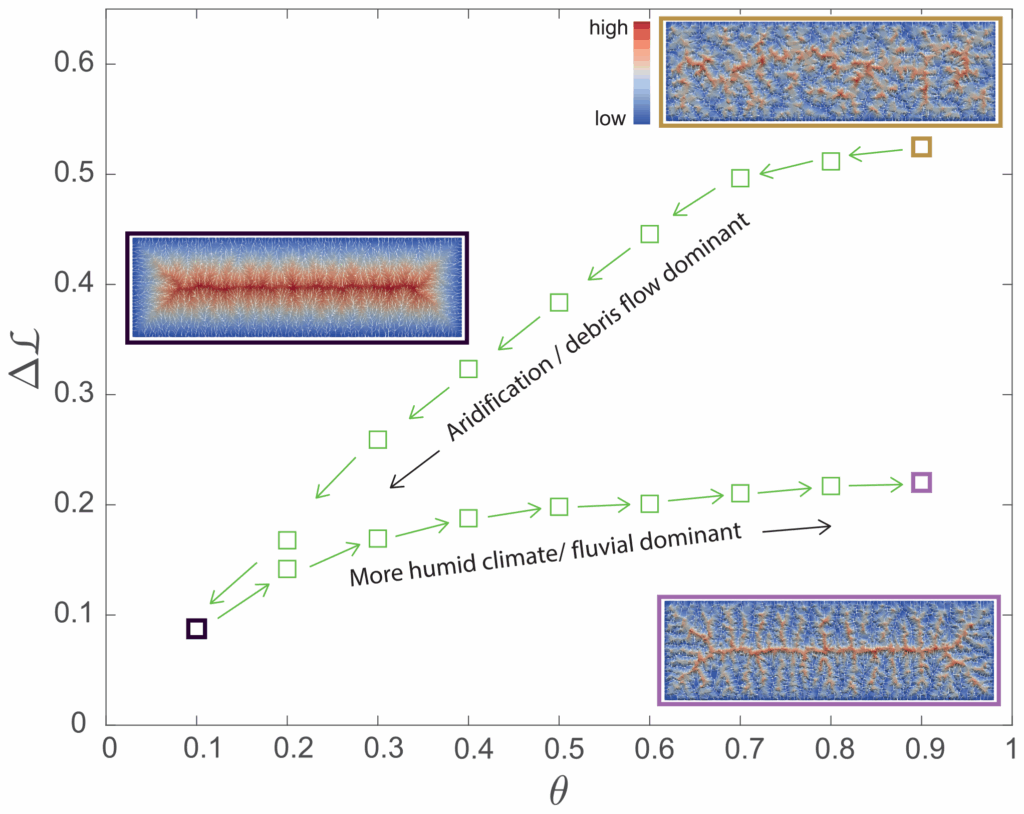
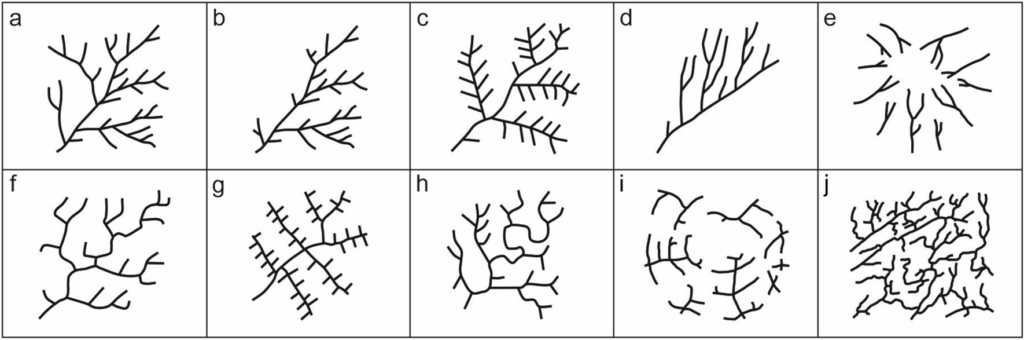
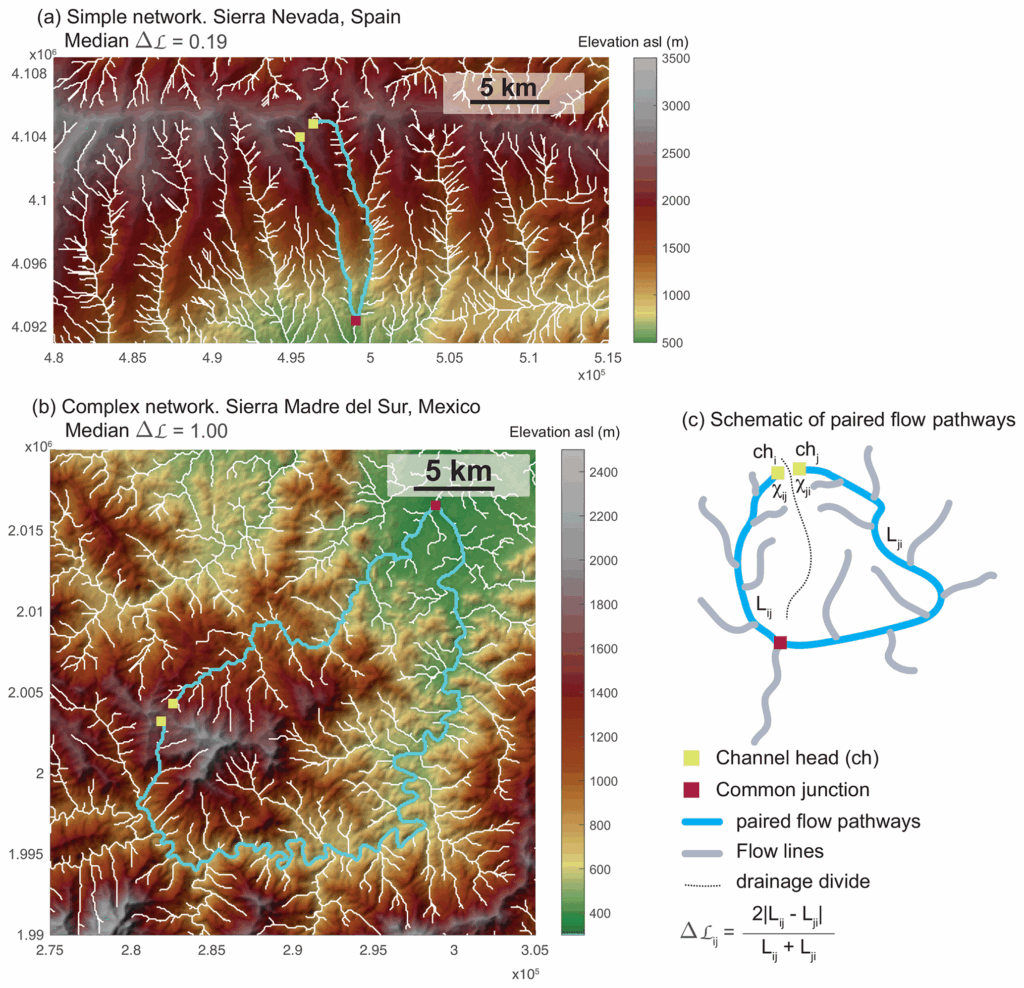
Drainage networks play a crucial role in managing surface water runoff and preventing flooding. One important aspect of drainage networks is their plan-form geometry, which refers to the spatial arrangement of channels and streams within the network. By understanding the plan-form geometry of drainage networks, engineers and planners can design more efficient and effective drainage systems.
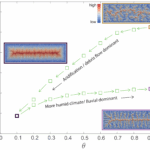
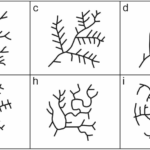
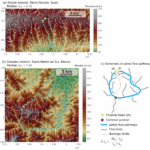
There are several key components of plan-form geometry that are important to consider when designing a drainage network. These include channel patterns, channel sinuosity, and drainage density. Channel patterns refer to the arrangement of channels within the network, such as dendritic, parallel, or trellis patterns. Channel sinuosity is a measure of how curved or straight a channel is, with meandering channels having high sinuosity and straight channels having low sinuosity. Drainage density is a measure of the total length of channels within a given area, and can help determine the overall efficiency of a drainage network.
Plan-form Geometry Of Drainage Networks
Benefits of Understanding Plan-form Geometry
By analyzing the plan-form geometry of a drainage network, engineers and planners can identify potential areas of concern and design solutions to improve the overall performance of the system. For example, a drainage network with high sinuosity channels may be more prone to erosion and sediment buildup, requiring additional maintenance and management strategies. Understanding the plan-form geometry can also help optimize the layout of channels and streams to maximize flow capacity and reduce the risk of localized flooding.
In addition, a better understanding of plan-form geometry can lead to more sustainable and environmentally friendly drainage designs. By incorporating natural features such as meanders and riffles into the network layout, engineers can create habitats for wildlife and improve water quality. Overall, by considering the plan-form geometry of drainage networks, designers can create more resilient and efficient systems that benefit both the environment and the communities they serve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the plan-form geometry of drainage networks plays a critical role in the design and performance of drainage systems. By analyzing channel patterns, sinuosity, and drainage density, engineers and planners can optimize the layout of channels and streams to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of flooding. Understanding plan-form geometry can also lead to more sustainable and environmentally friendly drainage designs that benefit both the environment and local communities. By considering these factors, designers can create more resilient and effective drainage networks that help manage surface water runoff and protect against flooding.
Download Plan-form Geometry Of Drainage Networks
A Novel Approach To The Classification Of Terrestrial Drainage Networks Based On Deep Learning And Preliminary Results On Solar System Bodies Scientific Reports
ESurf Channel Concavity Controls Planform Complexity Of Branching Drainage Networks